THE EARTH’S INTERIOR
The earth is made up of several concentric layers just like onion. But no factual evidence regarding earth’s interior is available. So for data, we have to depend on the indirect sources. These indirect sources are artificial sources and natural sources.
THE ARTIFICIAL SOURCES
- Density– The shape of the earth is near about spherical. By using the radius and mass the average density of the earth calculated to be 5.5 gm/cm3. The average density of the earth’s crust came out to be 2.6-3.3 gm/cm3. The core is much denser, the density is 11 gm/cm3.
- Pressure– Density is directly proportional to the pressure. That means density increases with the pressure. But in case of rocks,the density does not increase beyond the critical limit. This proves that the core of the earth is made up of heavy metals.
- Temperature– The temperature increases with depth. It rises 1°C for every 32 metres. But in the case of the earth, the rise in temperature is not uniform. For the first 100 km, the temperature rises by 12°C/ km and then 2°C for the next 300 km and after then 1°C /km. The heat flows from core to the surface of the earth in the form of convective currents.
THE NATURAL SOURCES
- Volcanicity– During volcanic eruption, the molten lava comes out the vent. This provides a shred of evidence that a layer beneath the crust is in the semi-solid state. This layer is called the magma chamber.
- Seismology– During an earthquake wave are generated these waves are called seismic waves. These seismic waves are recorded by a seismograph. The seismic waves are of three types-
- P/ Primary/ Compressional Waves– These waves exhibit the oscillator motion.
- S/ Secondary/ Transverse/ Shear Waves– These waves propagate transversely just like light through the earth.
- L/ Love/ Rayleigh/ Longitudinal Waves– These waves are called surface waves as they are confined to the surface of the earth.
- All these waves have different properties. It has enabled us in collecting the authentic informations about the earth’s interior.
- Snell’s Law– According to this law, ” the seismic waves are reflected when they strike between the interface between two materials drawing different elastic properties and densities.”
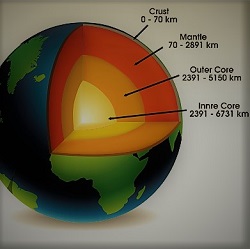
THE INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
On the basis of the seismic waves the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics has divided the interior of the earth into three zones. These zones are- the Crust, the Mantle and the Core.
- The Crust– The outer superficial layer of the earth is called the Crust or the Lithosphere. It is a relatively a thin layer. The thickness is about km but some researchers believe that it may extend to 100 km. The crust has been divided into two zones-
- Upper Crust– The upper crust extends up to 30 km and the density is 2.7-2.8 gm/cm3. The speed of the P waves is 6.1 km/sec in the upper zone.
- Lower Crust-The lower crust extends from 30km-100 km i.e 70 km and the density is 3 gm/cm3. The speed of the P waves 6.9 km/sec.
- A discontinuity exists between the upper and lower crust named the Conrad Discontinuity.
- The crust is made up of Silica and Aluminium therefore it is called SIAL.
- The Mantle– In the lower crust, the speed of the seismic wave increases suddenly to 8.1 km/sec. It happens due to a discontinuity, the Mohorovicic Discontinuity. Named after its discoverer A. Mohorovicic. The Moho discontinuity is between the upper mantle and the lower crust. From Moho discontinuity, the mantle extends to 2890 km. The mantle is divided into three zones. These zones are-
- The Upper Mantle– From Moho-400 km
- The Intermediate Mantle-From 400-1000 km
- The Lower Mantle– From 1000-2890 km
- The density of the Mantle varies. The density of the upper mantle is 3 gm/cm3 whereas the lower mantle is 4.5gm/cm3. The mantle occupies 82.54% of the total volume of the earth and 66% of the total mass of the earth. The Repetti Discontinuity is between the upper mantle and lower mantle. The speed of seismic waves decreases due to Repetti discontinuity. The major elements of the mantle are Silica and Magnesium. Therefore it is also called SIMA.
- The Core– In the lower mantle the speed of the P waves increases suddenly. This increase in the speed is due to the change in the density of the rocks. This change in the density results in a discontinuity, the Weichart Guttenberg Discontinuity. From Weichart Guttenberg discontinuity, the core extends up to a depth of 6371 km. The core is divided into two zones-
- Outer Core– From 2890-5150 km
- Inner Core-From 5150-6371 km
- The density of the core varies from 10-12.3 to 13.6 gm/cm3. The inner core is in solid-state due to high density and pressure. The outer core is in the molten state. The volume of the core is 16% to the total of the earth and the mass is 32% of the total mass of the earth. The Lehman Discontinuity is between the outer and the inner core. The chief elements of the core are Nickle and Iron. therefore it is also called NiFe.
- Barysphere– The term was earlier used for the whole core.
- Mesosphere-The area beneath the asthenosphere and includes the mantle completely.
- Asthenosphere– The layer immediately beneath the lithosphere that extends from 100-200 km is called Asthenosphere. A zone of low velocity. In comparison to the lithosphere, it is more plastic and less viscous. So it can easily change its shape without breaking. As the depth increases the pressure also increases. That results in an increase in the speed of the seismic waves. This layer is soft in comparison to lithosphere but still, it is more rigid than steel.