THE PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
The word Tectonic is originally a Greek word ‘ Tekton‘ means ‘Builder‘. The word builder is applied to the forces which form new features on the earth’s crust. It includes diastrophism( means- deformation of the earth’s crust especially by folding and faulting ). The theory of the plate tectonics was proposed in the decade of the 1960s. The term plate was first coined by J.T. Wilson in 1965. The phenomenon of the plate tectonics was first proposed by Harry Hess. His concept was based on the Sea Floor Spreading. But this concept was scientifically explained by Morgan, McKenzie, Parker and Holmes and others.
THE PLATE TECTONIC THEORY– The theory says that the crust of the earth is divided into fragments. These fragments are big and small and are called plates. The plates include both the continental as well as oceanic plates. These lithospheric plates are 100 km thick. The plates are placed over semi-solid or molten layer the Asthenosphere and the plates floating over it and are motion with respect to each other. The asthenosphere is composed of Silica and Magnesium hence called SIAL. These plates are important because all the tectonic activities such as volcanicity, seismic, mountain building and faulting occur along with the plates. The plate tectonic theory is supported by two scientific concepts- the Palaeomagnetism and the Sea-floor spreading. The former is the branch of geophysics that deals with the magnetism of the rock, induced in the rock by the earth’s magnetic field during their time of formation. The latter phenomenon occurs along with the weak plates. This results in the opening of a crack or a gap. The crack gets open and is filled by hot magma that is coming from the interior of the earth. It cools down and solidifies to form a new crust. The plates on either side drift away, the gap widens and the new crust covers the gap. This result in the growing of the ocean floor. This concept was given an American geologist Robert S. Dietz.
THE DIVISION OF THE PLATES
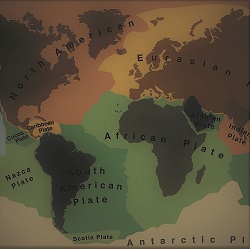
- MAJOR PLATES– The major plates are basically 6 in number. If North American and South American plates are mentioned separately then the number becomes 7. American Plate, African Plate, Eurasian Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate (the pacific plate is the largest plate, covers entire oceanic crust and 1/5th of the earth’s surface ) and Antarctican Plate.
- MINOR PLATES– The important minor plates are- Nazca, Arabian, Cocos, Philippines, Caribbean and Scotian.
TYPES OF PLATE MARGINS/BOUNDARIES
- THE CONSTRUCTIVE MARGIN/DIVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARY-when two plates drift apart a crack is developed. Through this gap or crack the molten magma oozes out to the surface and it cools down and solidifies. This results in the formation of the new crust. The plates are called divergent or accreting and found along the mid-ocean ridge. Example- The mid-Atlantic ridge is the best example formed due to divergence of the American, Eurasian and African plates.
- DESTRUCTIVE MARGIN/CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARY -In the destructive margin, the plates of different densities collide. The denser plate is subducted beneath the lighter plate. Benioff is the zone where subduction takes place. The subducting plate is lost in the mantle. Therefore the plate margin is called the Consuming Plate Margin. On the basis of the interaction between the plates, the destructive plate margin is of three types-
- Interaction between Continental Plate and the Oceanic Plate– The oceanic plate on being denser gets subducted below the continental plate. Hence trenches are formed. The Rockies and Andes mountains are formed as a result of continuous deposition of the sediments. In the Benioff zone, the volcanoes are found. Example- The Ring Of Fire is the best example of the interaction between two plates, the Pacific plate is subducted by the American plate.
- Interaction between Continental Plates– When the phenomenon of convergence occurs between two plates then a long chain of fold mountains are formed. This process is highly unstable. Example- The Himalayas are the young fold mountains, formed due to convergence of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate. The Himalayas are formed due to the folding of sediments lying in the depression of the Tethys sea (geosynclines)and folding of the plate margins.
- Interaction between Oceanic Plates– When two oceanic plates collide, the comparatively denser plate gets subducted. This result in the formation of Oceanic Trenches and volcanic islands is formed. Example- The chain of islands (festoons) and volcanoes is formed due to convergence of the Pacific plate with either Japanese or Philippines Plate in that region.
- CONSERVATIVE MARGIN/PARALLEL/TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY– The conservative margin is also called Shear Plate Margin. In this case, two plates pass or slide past each other. The crust is neither formed nor consumed. The faults are formed. Example-San Andreas Fault in California.